5 Strategic Shifts to Capture Shares in the $1 Trillion Global Chip Market
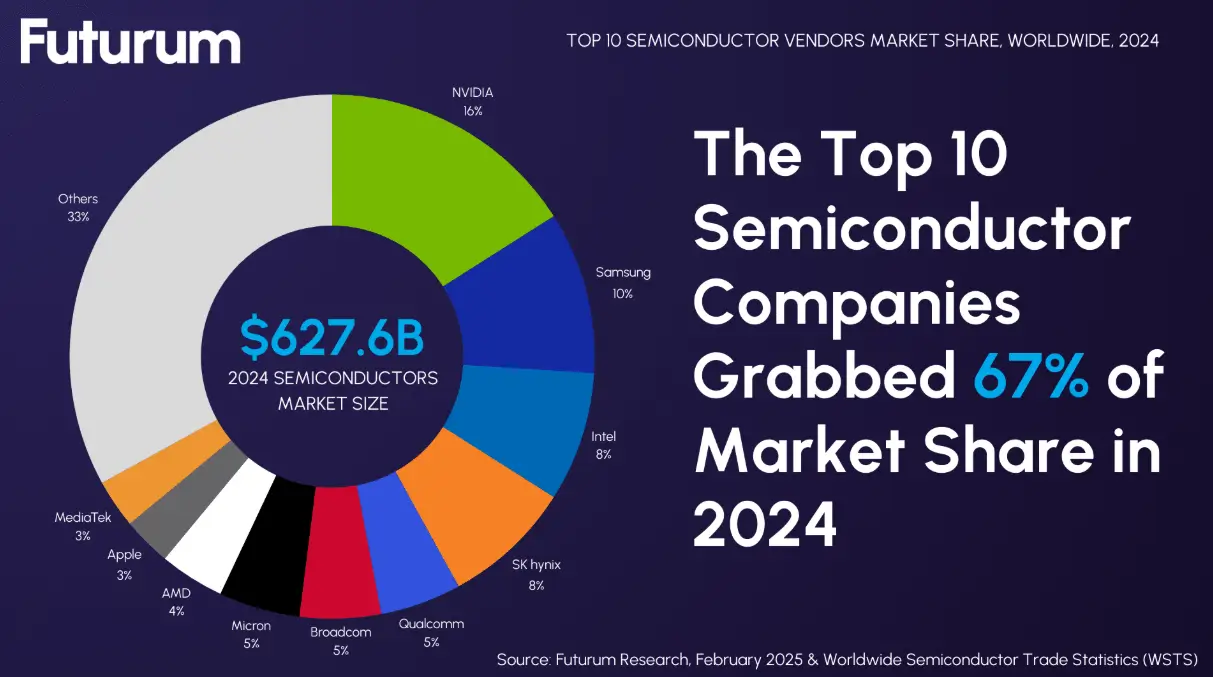
The semiconductor industry surged through 2024 with impressive momentum, posting 19% year-over-year growth and reaching US$627 billion in global sales, surpassing earlier forecasts.
Looking ahead, 2025 is projected to deliver even stronger performance with predicted sales of US$697 billion and a clear path to a $1 Trillion Global Chip Market by 2030. If the industry continues at just a 7.5% CAGR, it could double again by 2040 to reach US$2 trillion.
Behind these numbers lies a fundamental reshaping of the entire semiconductor landscape. Gen AI chips alone exceeded conservative forecasts, contributing more than $125 billion in 2024–over 20% of all chip sales–and are projected to exceed $150 billion in 2025.
Meanwhile, stock market valuations are echoing this momentum. The top 10 global chipmakers saw their combined market cap soar to US$6.5 trillion by the end of 2024, nearly doubling in a year. Companies riding the AI wave are outperforming dramatically.
The stakes are high. Companies that haven’t implemented at least three of the five strategic shifts outlined below may find it difficult to outpace competitors.
In this post, we’ll explore the semiconductor market outlook, the challenges ahead, and the five strategic pivots companies must make now to compete in the trillion-dollar chip economy.
Discover how yieldWerx can transform your semiconductor test data into smarter decisions and higher yields. Start your journey today by contacting us.
The Growth Story Has a Dark Side
While the semiconductor industry is experiencing unprecedented expansion, this momentum comes with complex, high-stakes challenges. How companies respond now will determine their ability to survive, scale, or surrender market share in the years ahead.
1) Physical Limits Are Closing In
For decades, Moore’s Law served as the semiconductor industry’s compass, enabling predictable performance gains through smaller transistors. But as chip features now approach just a few atoms wide, the laws of physics are pushing back.
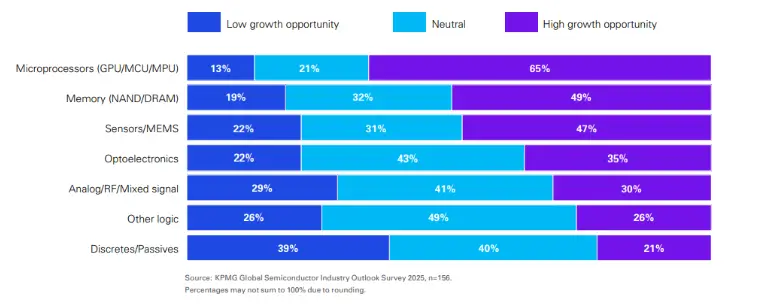
Power leakage, heat dissipation, and quantum effects are no longer theoretical, they’re operational hurdles. As traditional monolithic scaling reaches its limits, companies must look beyond node shrinkage to new architectures and heterogeneous integration techniques. This physical wall is not a slowdown; it’s a signal that the old playbook no longer applies.
2) The Fab Cost Explosion
Building a modern semiconductor fabrication plant has become a multi-billion-dollar endeavor. Where advanced fabs once cost under $5 billion, today’s most cutting-edge facilities can exceed $20 billion. That’s a 5X increase in just a decade, and it’s fundamentally reshaping industry dynamics.
Only a handful of players, those with massive capital reserves or government backing, can afford to stay in the game. This steep financial barrier is pushing smaller manufacturers and startups to the sidelines or forcing them into specialized niches. It’s no longer just about innovation, it’s about who can afford to manufacture at scale.
3) A Fragile Global Supply Chain
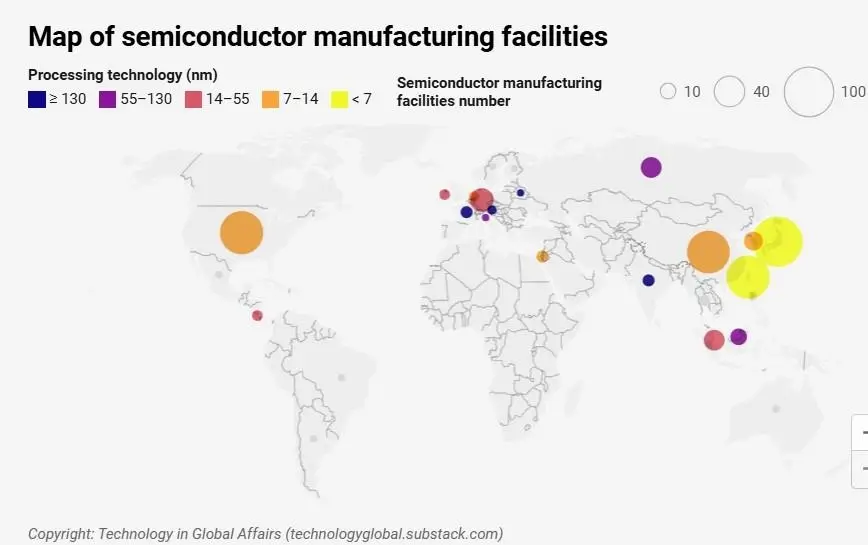
The pandemic, natural disasters, and geopolitical tensions have exposed the semiconductor supply chain’s vulnerabilities like never before. With so much manufacturing concentrated in a few regions, most notably Taiwan and South Korea, even a minor disruption can cascade through global production lines.
Trade restrictions, export controls, and national security concerns are adding new layers of complexity. Companies reliant on single-source suppliers or overseas fabs are rethinking everything from sourcing strategies to geographic footprints. Resilience, once considered a luxury, is now a competitive necessity.
4) The Talent Gap Is Growing
As chip design becomes more complex and diversified, the demand for skilled engineers is outpacing supply. There is a growing shortage of talent not just in R&D but across the entire value chain: from yield engineers and reliability specialists to software developers who can build the tools needed to analyze and optimize massive datasets.
Countries and companies are scrambling to develop talent pipelines, while the gap is widening. Industry projections indicate that by 2030, the global semiconductor sector will need to hire approximately 1 million additional skilled workers while also retaining its current workforce. Without the right people, even the best technology can stall.
5) Market Volatility and Economic Uncertainty
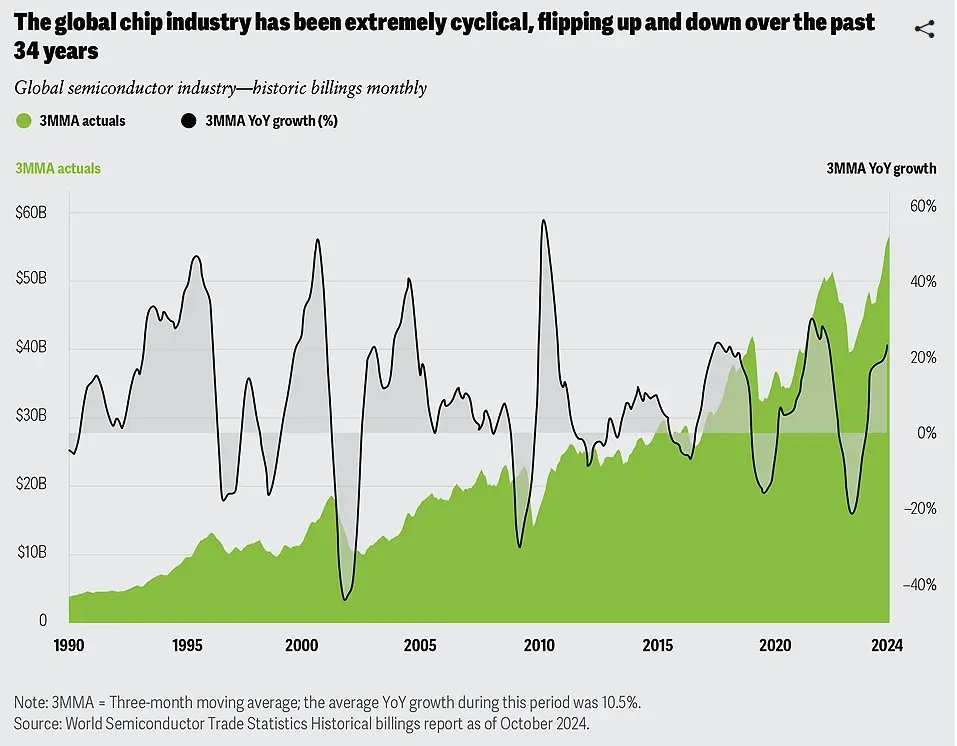
The semiconductor industry has always been cyclical, but recent years have introduced a new level of unpredictability. Shifts in consumer demand, inflation, monetary tightening, and geopolitical shocks are causing abrupt swings in production and investment decisions.
Inventory corrections are becoming more frequent, and forecasting has grown more complex as new markets (like AI accelerators) rapidly scale while others (like traditional computing or smartphones) slow down. In such a volatile environment, companies need the agility to pivot quickly and the visibility to make data-informed decisions at every level.
This leads us to the top five critical semiconductor strategy shifts that companies must embrace now to maintain a competitive edge. Waiting could mean falling behind as the industry continues to evolve at lightning speed.
Five Strategic Shifts Semiconductor Manufacturers Need to Implement Now to Compete in the $1 Trillion Market
1) Embrace Chiplets and Heterogeneous Integration
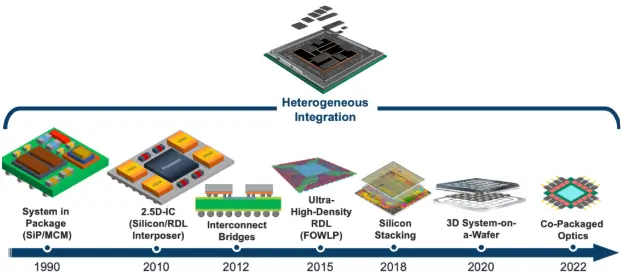
Chiplets are transforming how performance, cost, and time-to-market are balanced. This approach enables designers to mix and match specialized dies, whether it’s a high-performance AI accelerator, a power-efficient memory block, or a custom I/O interface. This results in dramatically reduced development cycles and increased flexibility to tailor chips for rapidly evolving applications.
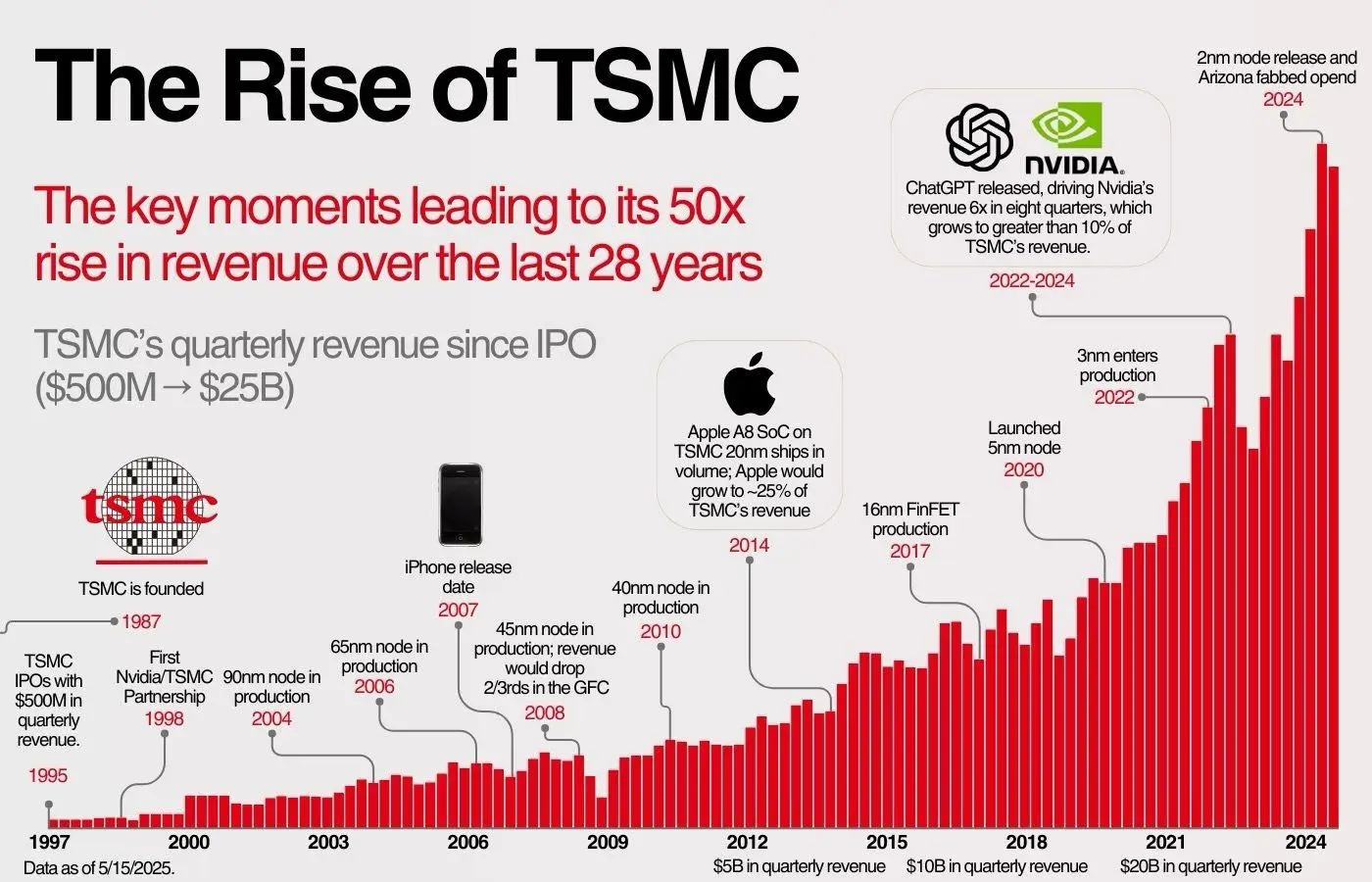
Major AI chip producers like AMD, Intel, and Nvidia are heavily investing in chiplet ecosystems and advanced packaging technologies, such as 2.5D and 3D stacking. It allows for superior performance per watt and opens the door for supply chain diversification, as different chiplets can be manufactured in separate fabs optimized for specific processes.
Companies that stick to traditional monolithic designs risk being left behind. They may struggle to keep up with the faster innovation cycles and greater scalability achieved by those embracing heterogeneous integration and next-generation solutions.
2) Invest in AI-Powered Automation
Artificial intelligence is no longer just an application for semiconductor chips. It’s a vital enabler of how chips are designed, tested, and manufactured. AI-driven automation accelerates defect detection, yield analysis, and predictive maintenance, often catching subtle anomalies invisible to human inspectors. Machine learning models optimize wafer processing parameters in real time, improving throughput and reducing yield losses.
Beyond manufacturing, AI tools are transforming chip design workflows by automating complex verification tasks and accelerating simulation times. This translates into faster time-to-market and higher design quality.
3) Commit to Sustainable Manufacturing: Driving Growth Through Green Innovation
Semiconductor fabrication remains one of the most resource-intensive manufacturing sectors globally. The pressure to reduce carbon footprints, conserve water, and minimize silicon waste has never been greater. Leading semiconductor manufacturers are setting ambitious sustainability targets. Intel aims for net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2040, TSMC is investing billions in renewable energy, and Samsung is adopting circular economy principles in wafer recycling.
Sustainability is now a strategic differentiator. Beyond regulatory compliance, companies demonstrating green leadership are attracting ESG-conscious investors and customers. Energy-efficient fabs not only reduce operational costs but also buffer against rising energy prices and supply disruptions. Emerging technologies, like AI-driven fab process optimization and advanced sensor networks, enable real-time energy and resource management.
4) Secure and Diversify Supply Chains
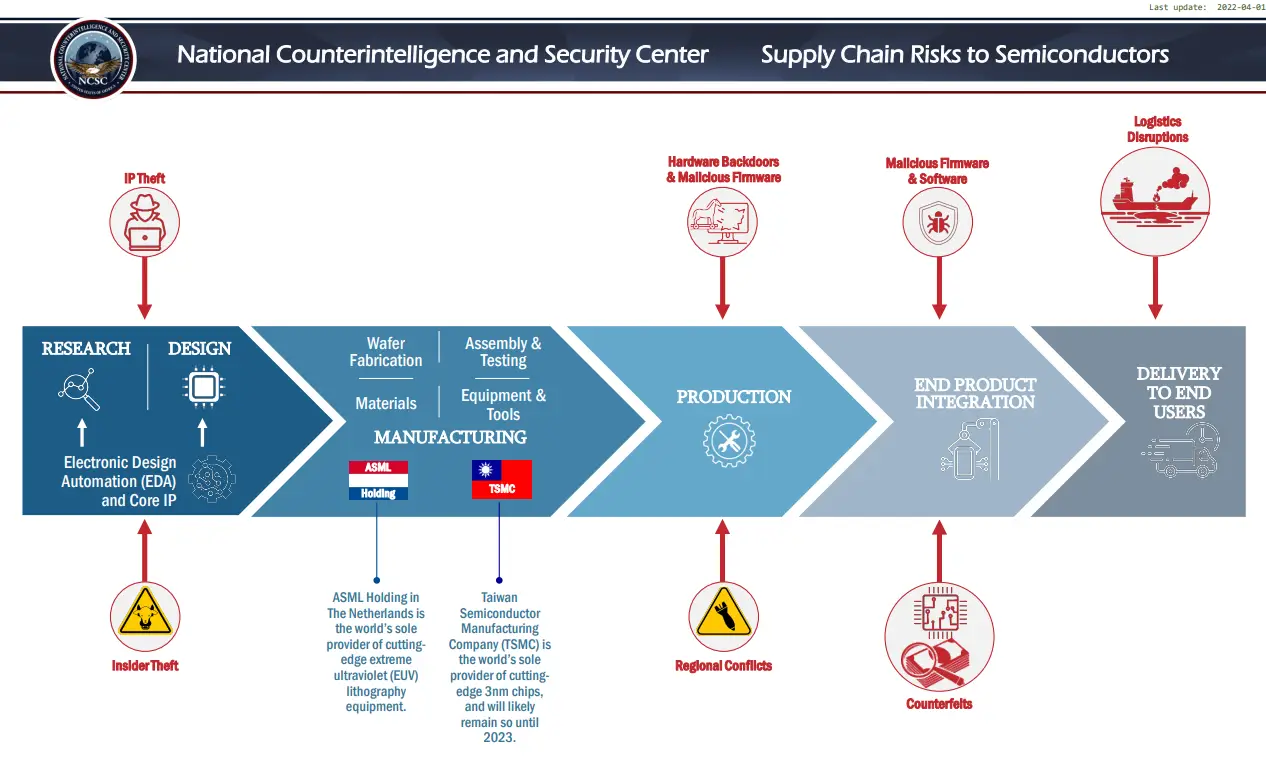
The semiconductor supply chain’s fragility has been spotlighted by recent global disruptions, from the COVID-19 pandemic to geopolitical tensions in critical regions. Concentration of manufacturing capacity in East Asia, particularly Taiwan and South Korea, poses significant risks. Reshoring and nearshoring of chip production is one of the top semiconductor trends. It bolsters security and reduces dependency on single points of failure.
Companies must rethink their entire supply chain strategy by diversifying suppliers, investing in buffer inventories, and sourcing alternative raw materials to mitigate scarcity. The adoption of digital twins, blockchain, and AI-powered analytics provides unprecedented transparency and predictive insight into supply chain health. These tools enable proactive risk management, anticipating disruptions before they escalate into costly delays.
Failing to diversify supply chains today could mean crippling semiconductor shortages tomorrow, affecting product launches, customer trust, and market position.
5) Prioritize Specialized Solutions in High-Growth Markets: Capturing the Next Wave of Demand
The semiconductor industry’s growth will increasingly hinge on how well companies can tailor solutions to rapidly expanding vertical markets.
- Automotive Electronics: Electric and autonomous vehicles demand chips that balance safety-critical reliability with massive computational power.
- AI Accelerators: Chips designed for machine learning inference are driving explosive growth in cloud and edge computing infrastructure.
- Healthcare Technology: Smart medical devices and diagnostics require highly specialized chips optimized for accuracy and low power consumption.
- Industrial Automation: Smart manufacturing is similarly accelerating demand for chips that enable real-time sensing, connectivity, and control.
Companies that recalibrate their R&D and go-to-market strategies to focus on these specialized domains will unlock higher margins and longer-term customer relationships. Generic, one-size-fits-all chips risk commoditization and lowering profits in an increasingly competitive landscape.
How Can yieldWerx Help You Stay Ahead of Your Competitors
Navigating the complex transformations shaping the semiconductor industry demands more than just visionary leadership. It requires access to the right tools, deep insights, and actionable data to execute strategies effectively and confidently. This is precisely where yieldWerx steps in as a game-changer.
Our cutting-edge yield analytics platform is designed specifically for semiconductor companies, offering tailored solutions that address the unique challenges of today’s dynamic market. From optimizing semiconductor yield through sophisticated data-driven analysis to seamlessly integrating vast volumes of test data, yieldWerx helps organizations unlock hidden efficiencies and improve decision-making across their operations.
Moreover, our platform enhances supply chain visibility, enabling companies to proactively anticipate disruptions. In a trillion-dollar semiconductor economy marked by uncertainty and fierce competition, partnering with yieldWerx means future-proofing your semiconductor strategies.
Contact Us Today and Learn More About Our Data Management Modules
Recent Posts
- 5 Strategic Shifts to Capture Shares in the $1 Trillion Global Chip Market
- Chiplets: The Building Blocks of Sustainability
- The Complete Guide to Wafer Defect Detection Using Knowledge Graphs in 2025
- AI-Powered PAT: A New Era of Smarter Manufacturing
- KLARF File Format: Enhancing Semiconductor Yield Analysis with yieldWerx