A Guide to Implementing Yield Management Software in the Semiconductor Industry
Optimizing yield is essential for operational efficiency and financial success. Yield management software significantly addresses these challenges, utilizing data analytics and machine learning to improve defect detection and process control.
This technology improves yield calculation flexibility and supports yield improvement by offering insights into the fabrication process, improving quality control, and reducing yield loss. Integrating real-time monitoring with statistical process control aids in making data-driven decisions and optimizing the chip manufacturing process.
Understanding the Yield Management Challenge
The production process in semiconductor fabrication is complex. It involves manufacturing integrated circuits on wafer surfaces.
This process, known as wafer fabrication, demands precision at every turn, with each chip layer carefully added, patterned, and etched to form the complex structures that make up modern electronics.
Wafer fab optimization is critical, as even minor defects in wafer fabrication can lead to considerable yield loss, increasing production costs and reducing profitability.
Key Terms in Yield Management
Understanding this process requires an understanding of a few important terms:
- Yield: The proportion of usable chips produced from a batch of silicon wafers. High yield rates are synonymous with efficiency and cost-effectiveness in chip manufacturing.
- Defect Detection: The process of identifying imperfections that occur during the fabrication process, which can lead to non-functional chips.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): A method used to monitor and control the fabrication process through data analysis, ensuring the process remains within predefined quality standards.
Factors Impacting Yield
Several factors influence yield in semiconductor manufacturing, making yield management a challenging yet vital aspect of the industry.
- Raw Materials: The quality of silicon wafers and other materials used in chip production can significantly affect yield rates. Imperfections in raw materials can propagate defects throughout the manufacturing process.
- Equipment Variations: Fluctuations in manufacturing equipment performance can introduce variability into the production process, leading to inconsistencies and potential yield loss.
- Process Control: Maintaining precise control over the fabrication process is essential. This includes temperature, chemical concentrations, and timing for each step. Effective statistical process control, supported by monitoring and SPC, is key for minimizing deviations and maximizing yield.
Optimizing Yield with Technology
Yield management software, using data analytics and machine learning, plays a pivotal role in addressing these challenges. It improves defect detection capabilities and provides comprehensive insights into process control, facilitating data-driven decision-making.
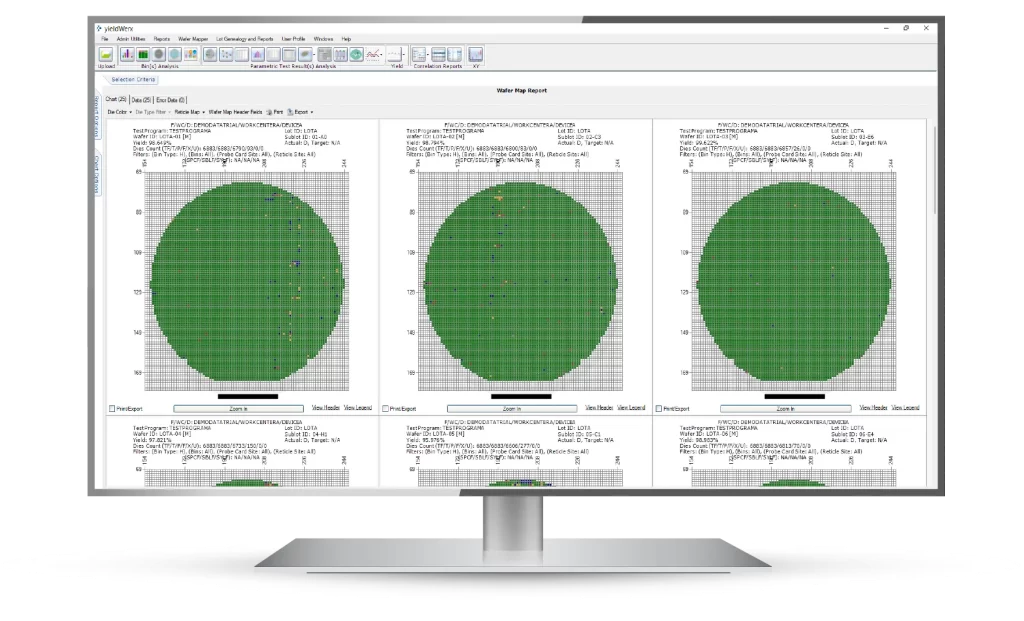
Yield management software integrates SPC data with live monitoring to offer an approach to wafer yield management that guarantees continuous improvement and yield optimization. This technology allows operators and engineers to observe the performance of manufacturing processes as they happen, enabling immediate detection and response to any deviations or anomalies.
This technology-driven approach, focusing on quality control and yield calculation flexibility, underscores the critical role of yield management in chip manufacturing.
How Yield Management Software Works
The semiconductor industry has made significant progress with yield management software designed to optimize wafer yield by employing various automation and analysis methods.
With its effortless integration with statistical process control systems designed for semiconductor manufacturing and its ability to infuse monitoring into the production process, this software is an invaluable ally in pursuing operational excellence.
Integration with Statistical Process Control (SPC)
A significant feature of this software is its integration with Statistical Process Control data and monitoring systems.
This combination allows for continuous oversight of the fabrication process, ensuring any deviations are quickly identified and corrected.
It’s an essential strategy for maintaining optimal process conditions and improving yield.
Advanced Capabilities
The ability to observe production metrics is a game-changer. It not only aids in the immediate detection of anomalies that could signal yield-impacting issues but also facilitates a proactive approach to managing production variables.
This yield monitoring guarantees that any deviation from the norm is identified and addressed, minimizing potential yield loss.
Automated Defect Detection
The software automates the detection and analysis of defects by utilizing machine learning. This capability is vital for identifying issues that might be overlooked manually, providing swift insights into potential problems.
Data Analytics and Visualization
Yield management software uses various data analytics techniques to convert enormous volumes of production data into valuable insights.
It finds patterns and trends through sophisticated analytics and visualization tools that may point to systemic problems or opportunities for process optimization.
This data-driven decision-making is essential to the fab’s ongoing progress.
Actionable Recommendations for Root Cause Analysis
Perhaps most importantly, the software provides actionable recommendations based on its analysis.
By employing advanced algorithms for root cause analysis it not only identifies the source of defects but also suggests corrective measures.
This capability is vital for implementing effective solutions that prevent the recurrence of the same issues, thus steadily improving yield over time.
Corrective Measures
Using the software’s insights, manufacturers can take exact corrective measures. These focused interventions—which can include changing material specifications, upgrading malfunctioning machinery, or modifying process parameters—are intended to directly address the root cause of yield problems.
Impacting Semiconductor Manufacturing
Yield Management Software is indispensable for semiconductor manufacturers, addressing critical defect detection and process control aspects.
It lays a foundation for sustained improvement, enabling manufacturers to optimize their yield effectively. Through detailed analysis and actionable recommendations, it helps maintain high quality, ensuring manufacturers stay competitive.
The semiconductor industry can achieve higher efficiency and improved profitability by embracing such advanced technologies.
Utilizing Yield Management Software: A Strategic Roadmap
Applying yield management software can significantly change the semiconductor manufacturing industry and help businesses become more profitable and efficient. However, a strategic approach is of the essence to unlock this tool’s full potential.
Here’s a roadmap for semiconductor industry leaders looking to implement yield management software effectively:
1. Define Clear Goals and Objectives
The journey begins with a clear vision. Company executives must be clear about what they aim to achieve through yield optimization.
This could range from reducing the defect rate and increasing the overall yield to improving process stability or shortening the time-to-market for new products.
Setting specific, measurable goals will guide the selection of the right yield management software and provide a benchmark for assessing its impact.
2. Evaluate and Select the Right Software Solution
It is important to select the most suitable yield management software. Solutions like yieldWerx™, renowned for its wafer fab optimization capabilities, offer a blend of features designed to meet the unique demands of semiconductor manufacturing.
Factors such as:
Compatibility
The software should smoothly integrate with existing systems, including SPC tools and equipment monitoring solutions.
Features
Prioritize software that offers extensive functionality, including real-time monitoring, advanced data analytics, automated defect detection, and actionable insights for root cause analysis.
Scalability
Choose a solution that can grow with your operations, accommodating production volume and complexity increases without compromising performance.
Support and Training
Ensure the provider offers robust customer support and training resources to facilitate smooth implementation and adoption.
3. Ensure Smooth Data Integration and Strong Infrastructure
Yield management software works best when it’s supported by a solid infrastructure and can easily share data with other systems within a company.
It is also essential to implement stringent security protocols to protect sensitive production data and intellectual property. This includes data encryption, access controls like multi-factor authentication, cloud firewalls, and regular security audits.
The Future of Yield Management
The future of yield management in the semiconductor industry is heading towards cloud-based solutions, promising a revolution in yield optimization through improved scalability, accessibility, and data analytics efficiency. These cloud platforms offer adaptive resource adjustment to meet fluctuating demands without hefty initial investments, coupled with global access to vital data and analytics tools for improved collaboration and faster decision-making.
Advanced analytics and data processing on the cloud enables the identification of issues affecting yield. At the same time, machine learning and AI technologies promise to automate decision-making and optimize yield strategies by analyzing patterns in historical data.
This shift provides semiconductor companies with a significant competitive advantage by enabling rapid scaling, remote data access, and sophisticated analytics and positions them for leadership in innovation and efficiency. As cloud-based yield management solutions evolve, they are set to unlock unprecedented performance and profitability levels, marking a new era of growth and innovation in the semiconductor sector.
Conclusion
Leaders in the semiconductor business who want to gain a competitive edge must implement yield management software as a strategic necessity, not just a tactical one.
With its extensive capabilities, from yield calculation flexibility to advanced defect detection, this technology is pivotal for ensuring operational excellence and sustained profitability.
For those ready to explore the potential of yield management software, scheduling a demo with yieldWerx can be the first step towards transforming their manufacturing landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the important features I should look for in yield management software?
When selecting yield management software, prioritize features that enhance operational efficiency and yield optimization. Key features include:
- Advanced analytics and visualization
- Real-time monitoring capabilities
- Automated defect detection
- Statistical process control (SPC)
- Integration with existing systems
- Scalability for future growth
2. Does implementing this software require significant IT infrastructure changes?
It depends on the software. Cloud-based solutions may require minimal changes, while on-premises solutions could need substantial changes to the existing IT infrastructure.
3. How can I measure the ROI of adopting yield management software?
Measure ROI by comparing pre and post-implementation yield rates, cost reductions in production, efficiency gains, and any reductions in waste or rework.
4. What are the best practices for training my team to use this technology effectively?
- Start with in-depth training sessions
- Use real-life scenarios for hands-on practice
- Provide ongoing support and advanced training
- Encourage feedback for continuous learning
5. Can I integrate yield management software with existing tools and systems?
Yes, most yield management software is designed to integrate with existing manufacturing execution systems (MES), ERP systems, and other production tools for seamless operations.
Recent Posts
- A Guide to Implementing Yield Management Software in the Semiconductor Industry
- Best Practices for Sensing Failures in Automotive ICs
- Why is Semiconductor Wafer Inspection Important?
- Multi Variant Part Average Test (MVPAT) for Refined Semiconductor Chip Manufacturing Analysis
- Wafer Map Calculators: Things You Should Know